 Relevancy and Engagement
massachusetts.agclassroom.org
Relevancy and Engagement
massachusetts.agclassroom.org
Charting Agricultural Careers
Grade Level
Purpose
Students will use infographics and charts to explore the careers that produce food, clothing, shelter, and fuel along with a variety of agricultural STEM careers requiring critical thinkers and problem solvers. Grades 6-8
Estimated Time
Materials Needed
- Computers with Internet access
- Access to Agcareers.com website
- Direct links to download high resolution infographics
- Top Agricultural Careers in Ag Business
- Top Agricultural Careers in Environmental Services
- Top Agricultural Careers in Food Science
- Top Agricultural Careers in Ag Mechanics
- Top Agricultural Careers in Plant Science
- Top Agricultural Careers in Natural Resources
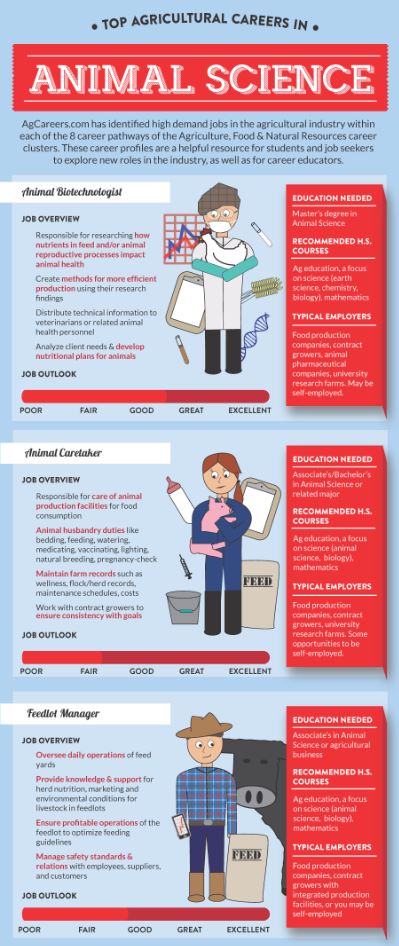
- Top Agricultural Careers in Animal Science
- Top Agricultural Careers in Aquaculture
- Optional: Computers with Microsoft Office Programs or substitute Google Office Software
Vocabulary
agriculture: the science or practice of farming, including cultivation of the soil for the growing of crops and the rearing of animals to provide food, wool, and other products
Did You Know?
- Agriculture and its related industries provide 11 percent of U.S. employment. (Close to 22 million jobs)1
- Of the 22 million agriculture-related careers in the U.S., only 2.6 million are direct on-farm jobs.1
- Food service, eating, and drinking places account for the largest share of agriculture-related careers and provide 12.5 million jobs.1
Background Agricultural Connections
Everyone has a connection to agriculture. Because agriculture is the endeavor that supports everyone’s basic needs (food, clothing, and shelter), innovations in agriculture have been a result of the integration and application of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). In agriculture there are five CTE Career Pathways: Agricultural Systems Technology, Animal Science, Food Production and Processing Systems, Natural Resource Systems, and Plant Systems. Within these CTE Pathways you will find the career of farmer and rancher. Over the last two centuries, the number of farmers and ranchers needed to produce food, clothing, and shelter has decreased. The number of farmers and farm workers in the US workforce fell from a high of 98% in 1776, to 12% in the 1950s, to about 2% today. How is this possible? The US population has grown from 76 million in 1900 to 316 million in 2013. With this growth in population why are there fewer farmers and ranchers? The answer, STEM innovations related to on farm production and the growth of agricultural businesses to distribute agricultural goods and services.
To meet our current and future needs, agricultural STEM innovators (scientists and engineers), implementers (technicians), and agricultural business leaders are needed to fill a variety of agricultural careers. These innovators, implementers, and leaders will need to think critically and solve problems related to our everyday survival.
Each year the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), and the United States Department of Labor gather massive amounts of data. The USDA gathers consumer information, producer data, production data, and economic data. The Bureau of Labor gathers data about America’s workforce. Specifically, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (part of the Department of Labor) is the principal Federal agency responsible for measuring labor market activity, working conditions, and price changes in the economy. Much of the data collected by these agencies is quantitative and is presented in a variety of chart or graphs. In this lesson, students will explore specific agricultural careers by interpreting infographics that present “career findings” through images, graphs, and charts. Most agricultural jobs are STEM related and the “M” or mathematic component requires that students be able to collect data, analyze the data, and present findings for others. This lesson engages students with infographics and introduces them to the types of charts and graphs used in and used to define agricultural careers.
Engage
- As a class, review the agcareers.com home page.
- Allow various students to navigate through the site by scrolling through the “Featured Jobs” and then browsing the jobs using the world map. Look at other places around the globe, before looking at the United States.
- Investigate opportunities in areas of the United States known as large agricultural areas (e.g., the Midwest and California) before looking at your home state.
- Discuss any patterns or information that surprises students.
Explore and Explain
Activity 1: Exploring Top Careers in Agriculture
- Navigate to the Infographics page of the AG Careers.com website (under Job Seekers > Resources). This page includes numerous infographics categorizing the “Top Agricultural Careers in ….”
- Review with students one of the infographics and discuss the types of charts or graphs used on the infographic.
- Tip: To download a high resolution image of the infographic to view on the screen, click on the “print icon” on each infographic page. This will save the image to a location on your computer, desktop or downloads; the image will not print until you open the downloaded jpg image. Students will be able to see all the detail/text of the infographic if the file is downloaded.
- Tip: If students are not sure of the type of chart or graph (e.g., bar graph, pie charts, line graph, pictograph, flow chart), refer to the Types of Graphs website to aid in their understanding. These types of graphs are used in every discipline and career. If students are struggling with these basic graphs, take time to explain how each one is used.
- Put students into groups of two and assign each group a “Top Agricultural Careers in …” infographic. Ask each group to review their infographic and determine (think about) the type of graph or chart used, if any other type of chart or graph could be used, and what the chart or graph is telling them about the careers in the specific area.
- Note: Assign groups a variety of career-area infographics. It is recommended to begin with the 8 infographics listed in the Materials list, then add additional infographics according to student interest and class size.
- Ask each group to meet (pair) with another group and discuss their infographics with each other, discussing the types of charts/graphs and what the infographic is saying.
- Ask each group to share their infographic with the entire class stating what they learned about the careers in their infographic that they did not know before.
Activity 2: Exploring Career Profiles
- Place students into groups of two. Ask each group to navigate to the Career Profiles page of the website. This page includes the career profiles of more than 100 agricultural careers.
- Ask each group to select two careers from this page, and one job posting from the Featured Jobs. Ask students to explore the careers by comparing and contrasting the jobs, noting similarities and differences (i.e., education, experience or training required, salary, and the job outlook).
- Allow each group to share and elaborate on their exploration.
Elaborate
-
Develop your own or have students develop infographics about specific agricultural careers of particular interest. The following resources are a sampling of those available for developing your own infographics:
- Microsoft: Word, PowerPoint, Excel - Chart or Smart Art Tools
- Infographic Online Tools: http://bit.ly/1qToziK
- http://www.easel.ly/
- http://piktochart.com/
- http://nces.ed.gov/nceskids/createagraph/
- https://infogr.am/
- http://www.chartgo.com/
- http://www.gliffy.com/
- Other mobile device/tablet apps are available
Evaluate
- To assess student understanding of charts and graphs related to agriculture, search Google images with this term “agricultural graphs.” Randomly select a few of the charts or graphs and ask each student or group to explain what each chart is saying (this can be done orally or as a written assessment).
- After conducting these activities, review and summarize the following key concepts:
- Agriculture is the endeavor that supports everyone’s basic needs (food, clothing, and shelter).
- To meet our current and future needs, agricultural STEM innovators (scientists and engineers), implementers (technicians), and agricultural business leaders are needed to fill a variety of agricultural careers.
- These innovators, implementers, and leaders will need to think critically and solve problems related to our everyday survival.
Recommended Companion Resources
- Ag & Food Careers
- Careers Ag Mag
- Careers in Agriculture
- Corteva Grows Science: Outreach Career Paths
- Employment Opportunities for College Graduates in Food, Renewable Energy, and the Environment
- Field to Film Career Snapshots
- Food and Farm Facts Booklet
- Food and Farm Facts e-Learning Module
- Pathful Connect
- Seed Your Future